| Login | ||

Healthcare Training Institute - Quality Education since 1979
CE for Psychologist, Social Worker, Counselor, & MFT!!

Section 10
Anger Management Model Workbook
Question 10 | Test | Table of Contents | Printable Page
A key tool in managing emotions is found in the T.I.E Model for Anger Management. You experienced it with JACK, CLIENT and Eli, Therapist now it is presented as a pure theory uncluttered with dialogue. This anger management model includes nine exhibits providing a systematic process for learning this simple but powerful model. Although at first it may look intimidating, but as JACK, CLIENT experienced, it is really quite simple and it absolutely works. It will change your life!
How to use this workbook model:
Go through each exhibit. First look at the model and notice how it has changed from the previous exhibit. Then read how it works and complete the small exercise that is associated with each exhibit.
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
How it Works:
Because of important events, all humans have certain feelings. These next exercises will provide a framework to assist you in managing strong emotions; not to deny but to manage them.
Exercise:
Think of a time when you became angry, lost it, locked your jaws, and got very uptight! It does not have to be a recent event, just memorable. Write down a thumbnail sketch of the event. Briefly, what happened?
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model

How it Works:
The major words in the feeling language are Mad, Glad, Sad, Fear, and Hurt. The feeling list on page 96 has five columns with one of these words at the top of each column. This chart represents the rainbow of emotions available to be experienced in the human condition.
Exercise:
Have the event that made you angry have firmly in your mind, and then look at the mood chart to find which feelings you were experiencing (use only words on this list).
Write down all the feelings you were experiencing. First list the "Mad" feelings, then in a separate column write all the other feelings you experienced under the Sad, Fear, and Hurt columns on the feeling chart. Spend some time identifying what emotions you experienced.
Mad |
Other Feeling |
|
|
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
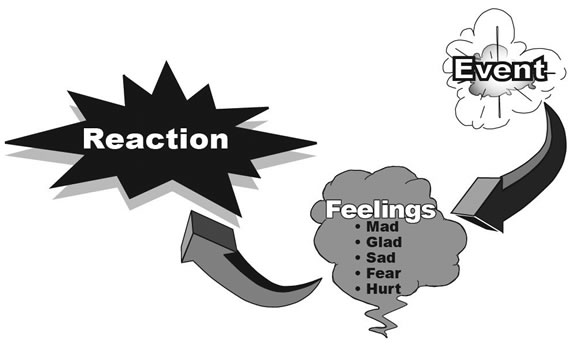
How it Works:
When a person experiences an event, various feelings are generated. With strong feelings, an equally strong reaction often occurs when something is said, or other action is taken, that would not have happened with a cooler mind. The reaction could be something said that is not really meant, a physical attack, or maybe the silent treatment.
Exercise:
What was your reaction to the identified event in the previous example? If you were observing YOU, what would you have witnessed? Did you yell, try to hurt someone else, run, get silent, plan revenge, or act out in some other equally dramatic way?
If you were observing you, what would you have seen?
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
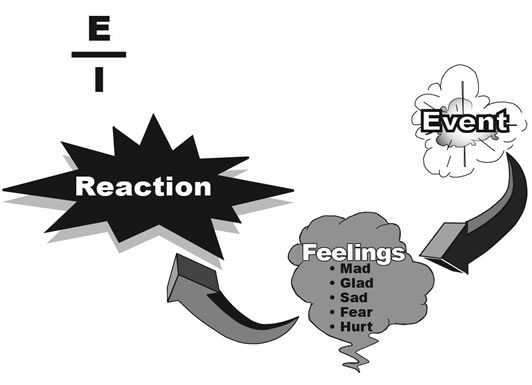
How it Works:
Unmanaged emotions create a reaction where there is a distinct possibility of hurting others emotionally, physically, and/or spiritually. This creates the condition where emotions are controlling intelligence, or as stated in the model above, "E over I".
When a person’s emotions are controlling them, it is very similar to a person drunk with alcohol. For the purposes of this lesson, people who are "E over I" are labeled "emotionally drunk".
Exercise:
Think of all the damage you have done to people you care about, and to yourself when you have been emotionally drunk.
Has being emotionally drunk ever worked toward building successful relationships? Maybe, but is there a better way?
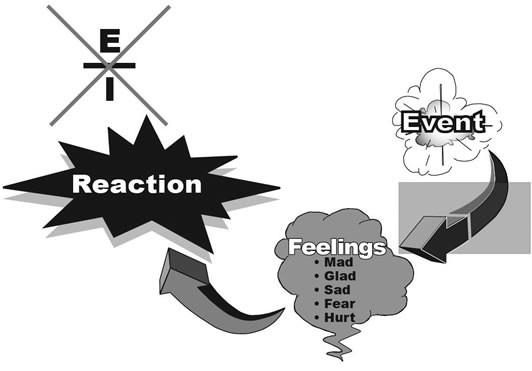
How it Works:
How often have you ever heard someone say, "He makes me so angry!" or "She irritates the fire out of me!" Would you like some freedom? The truth is no one (drum roll please) no one can make you angry; no one can irritate you!
By now you may want your money back on this book, but please do not reject this wonderful but simple truth. No one is in control of your emotions but you. Now that is freedom!
Exercise:
Do you want to continue reacting, or should a big red "X" be drawn through the E over I? Do you want to live emotionally drunk or emotionally sober? Your choice.
Now look at the line between the Event and Feelings on the diagram above. What happens between the event and a person’s feelings? Saying it a different way, a person’s emotions, or feelings are based upon something that happens in the brain. What are emotions or feelings based upon? Take a guess.
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
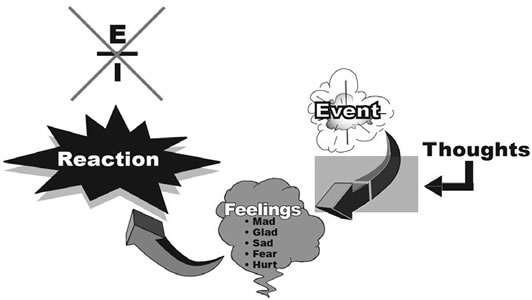
How it Works:
You guessed it — T H O U G H T S ! A person’s thoughts cause emotions. When experiencing the identified event, certain thoughts are generated about that event, and those thoughts generated certain feelings. If we are not careful; BO OM, we have a reaction!
Exercise:
Holiday—No exercise required.
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
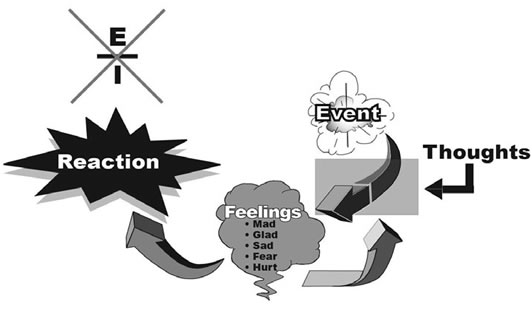
How it Works:
Look at the angry feelings listed under the Mad section. These are what we call "surface feelings". They are like the tip of the iceberg, what you see and observe. Under the angry feelings, there are other emotions as found in the Sad, Hurt, and/or fear columns. These other feelings are what is driving the strong reaction called anger.
Exercise:
Look at the feelings you listed in Exhibit X. Remember, you put the angry ones in one column and all the rest in another. Look at all the feelings not listed in the angry column. Identify the main feeling(s) driving your reaction. What feeling(s) has the most energy or best describes your emotional state? Select one or two.
Now think . . . what were the thoughts that were causing you to feel that emotion? Write your thoughts down.

There is a very good reason to separate the angry feelings as listed under the Mad column from the other columns of feelings. Anger is a surface feeling. Just like the iceberg, what you see is only the tip of the iceberg showing out of the water with most of it hidden beneath the water. In order to identify the strongest emotions driving our anger, we must dive beneath the waves and explore the Hurt, Fear, and Sad feelings.
MAD |
GLAD |
SAD |
FEAR |
HURT |
Agitation |
Admiration |
Abandoned |
Alarm |
Aloof |
Angry |
Affection |
Agonized |
Anxious |
Ashamed |
Annoyed |
Ardor |
Bored |
Apprehension |
Belittled Therapistttled |
Antagonism |
Confident |
Crushed |
Bashful |
Burdened |
Arrogant |
Cordiality |
Deflated |
Bewildered |
Cheated |
Bitter |
Curiosity |
Depressed |
Cautious |
Contempt |
Contempt |
Delight |
Disconnected |
Confused |
Denied |
Defiant |
Desire |
Disparaged |
Distraction |
Deserted |
Disapproving |
Devotion |
Distant |
Dread |
Disappointed |
Disdain |
Ecstasy |
Distraught |
Embarrassed |
Dismay |
Disgust |
Ecstatic |
Distressed |
Envious |
Embarrassed |
Disgusted |
Elation |
Downcast |
Evasive |
Exhausted |
Enraged |
Enthusiasm |
Forlorn |
Fearful |
Guilty |
Flustered |
Excitement |
Gloomy |
Flustered |
Humiliated |
Frustrated |
Fervor |
Grieving |
Frightened |
Hurt |
Furious |
Flush |
Helpless |
Horrified |
Insulted |
Hostile |
Generosity |
Hopeless |
Hysterical |
Lonely |
indignant |
Happy |
Ignored |
Inadequate |
Mean |
Irritated |
Hope |
Isolated |
Insecure |
Pain |
Livid |
Hopeful |
Jealous |
Menaced |
Pained |
Mad |
Inspiration |
Melancholy |
Overwhelmed |
Regret |
Mischievous |
Love-Struck |
Miserable |
Panic |
Shame |
Rage |
Passion |
Mournful |
Pathos |
Suffering |
Resentful |
Pride |
Remorse |
Shock |
|
|
Sympathy |
Sad |
Shocked |
|
|
Thrilled |
Unwanted |
|
|
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
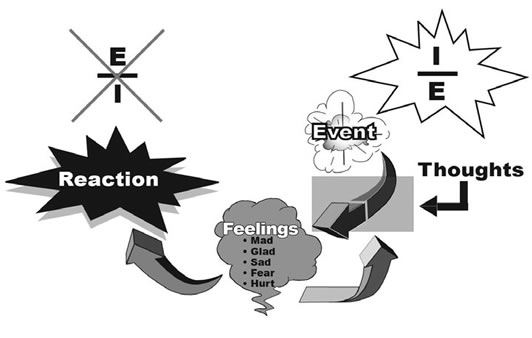
How it Works:
Once a person understands the thoughts that are driving their feelings, their intellect is now in control, and they are managing their emotions.
When managing emotions, that person is "I over E"; they are emotionally sober.
Exercise:
Take a deep breath. What often causes stress in people’s life is that they do not know they have options. When you learn this technique, you now have choices. You can choose to be emotionally drunk or emotionally sober.
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
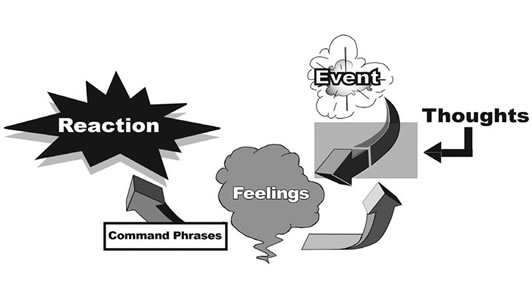
How it Works:
Go back to your anger incident previously identified.
In that anger incident you described, you were loaded with strong emotions that you probably did not manage well. When we react in the "emotionally drunk" state, allowing these emotions to be in control, we get the tag of "RUI" (reacting under intoxication). Often when we are in RUI", there is some illogical thinking associated.
Exercise:
What were you saying to yourself when you were so full of emotions?
List some of those thoughts.
T.I.E. – Anger Management Model
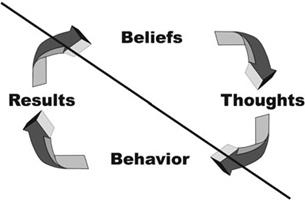
Command Phrases
Because of emotional learning, what we state to ourselves or to others when we are emotionally drunk becomes learned truths, indelibly printed in our minds, a very powerful form of learning.
This learning becomes our reality; out beliefs are based upon our thoughts and behaviors, as shown in the BBC
Model to the right.
Faulty belief results in harmful behaviors that we are often not able to see.
Review your Command Phrases, what would your behavior be if any one of these were your beliefs? Knowing where certain beliefs come from allows us to challenge them, thus freeing us from their control. This allows us to have a happier and more satisfying life.
When we are highly charged with emotions, our learning becomes sharper. Remember where you were and what you felt during 9-11. What we state to ourselves or express to others when we are full of emotions, as in being "emotionally drunk", becomes permanently printed in our mind. This is a very powerful form of learning. This learning becomes the reality upon which our beliefs are based. Thoughts come from beliefs and it is our thoughts dictating behavior.
Review the thoughts you listed on the previous page when you were RU I. What behavior would likely come from those thoughts? Knowing where certain beliefs come from enables us to challenge them, thus freeing ourselves to live happier and more satisfying lives. The entire purpose of this book is improving your life by the skill necessary to manage powerful emotions.
Sample Command Phrases:
I can’t do anything right"
"Don’t depend upon anyone."
"I try and I always fail"
"I have more problems that I can solve."
"I’m so stressed out ."
"I’m going crazy."
"She’s such a bitch."
"He is driving me nuts."
"They are out to get me."
"I can’t take it!"
"I can’t control my emotions."
"I’m at the end of my rope."
"I hate my job."
"The people here are all losers."
"No one can push me around."
"No one listens to me."
"They always get their way."
"My boss is such a jerk."
QUESTION 10
Faulty belief results in harmful behaviors that we are often not able to see. Knowing where certain beliefs come from enables us to challenge them, thus freeing ourselves to live happier and more satisfying lives. The entire purpose of this book is?
To select and enter your answer go to Test.
Test for this course
Forward to Section 11
Back to Section 9
Table of Contents
Top


